Neural organoids are three-dimensional, self-organizing cellular models generated from human pluripotent stem cells or primary tissues. Because these advanced 3D models can recapitulate many features of the human brain in vitro, neuroscientists are increasingly relying on neural organoids to investigate neurodevelopmental pathways, establish phenotypic models of disease, examine the impact of neurotoxicants, and explore unprecedented therapeutic strategies including precision and neuroregenerative medicine.
Featured on this page:
New! Organoid MEA Plates
The Maestro MEA platform continues to evolve with specialized tools designed to meet the unique demands of 3D organoid research. From flexible electrodes to guided placement, each new plate expands what’s possible when measuring function in complex biological models.
3DMap – Coming soon!
3DMap is designed to interface with 3D organoids like never before, using flexible electrode technology to capture signals across the surface without compromising its form.
Key Features:
- >> Flexible electrodes wrap around and interface with organoids
- >> Single well format (64 electrode)
- >> Transparent bottom
Compatible with: Maestro Pro, Edge, and Volt
Requirements: MEA Creator Kit
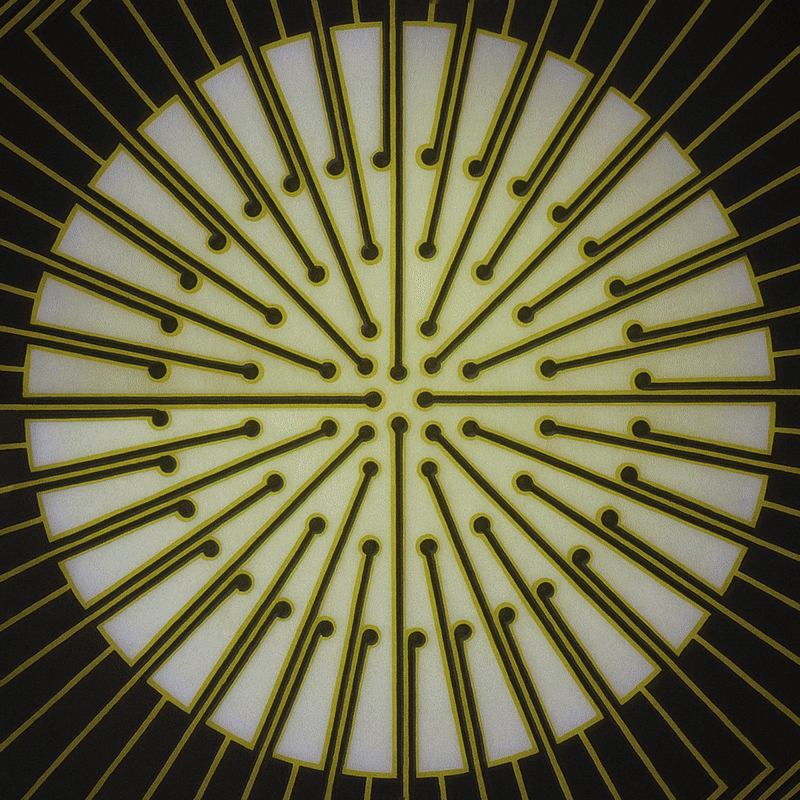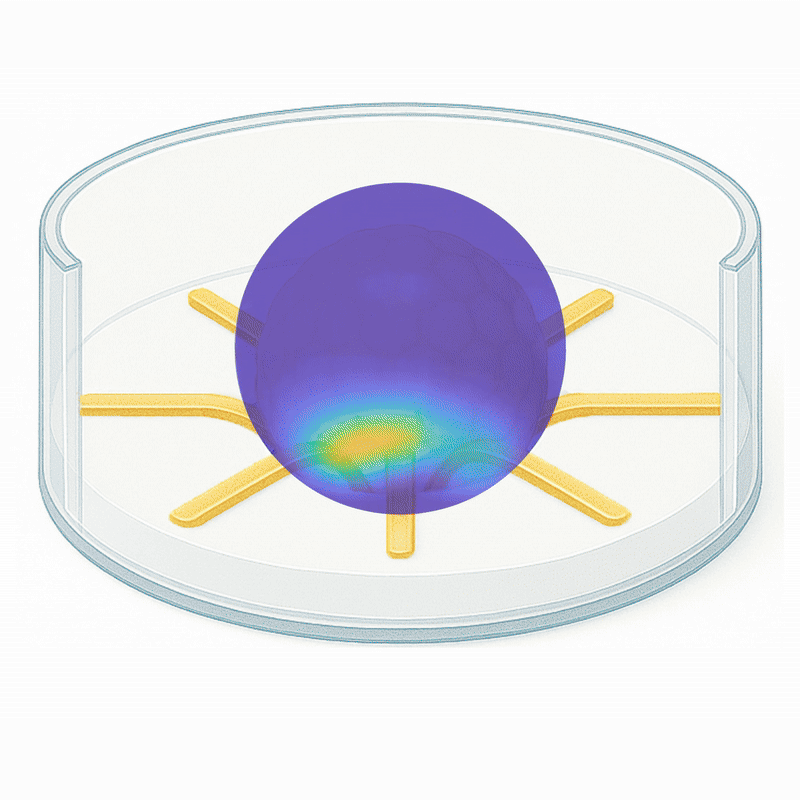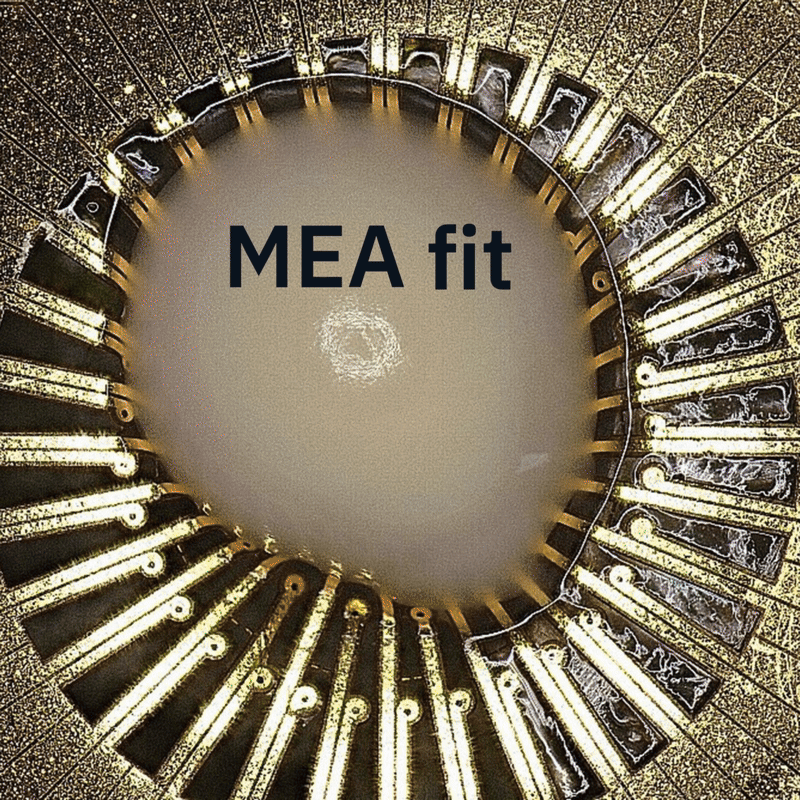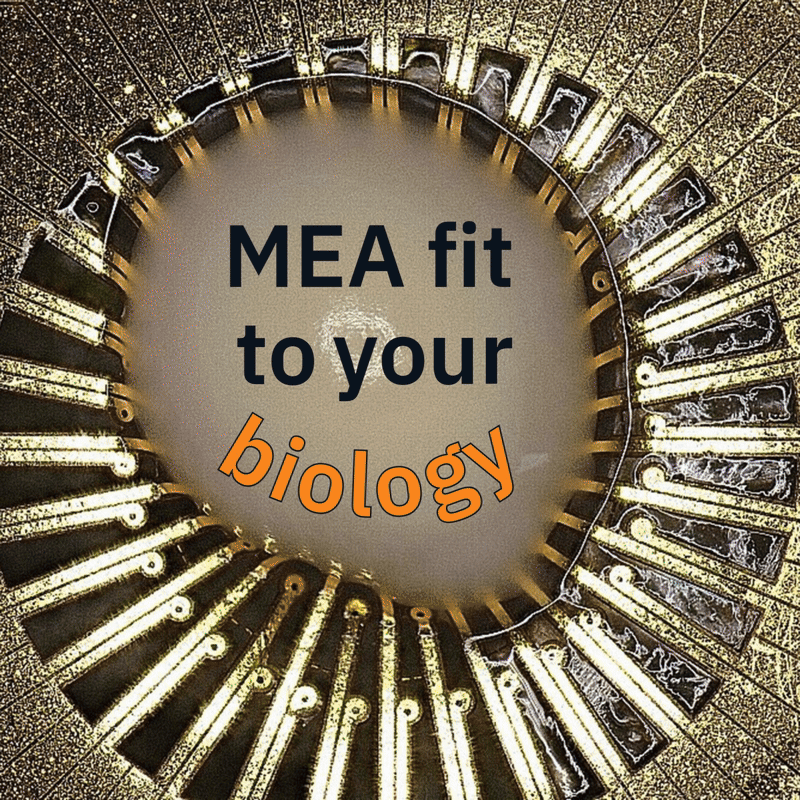
SpheroGuide
Easily plate large organoids over the electrode area. Designed to improve accuracy, efficiency, and reliability.
Key Features:
- >> Integrated placement funnel
- >> 48-well format (16 electrode/well)
- >> Transparent bottom
Compatible with: Maestro Pro

SpheroHD – Coming soon!
Easily plate small organoids and spheroids over the electrode area. Designed to improve accuracy, efficiency, and reliability.
Key Features:
- >> Dense electrode spacing (50 µm)
- >> Integrated placement funnel
- >> 1 well/4-microwell format (16 electrode/microwell)
- >> Transparent bottom
Compatible with: Maestro Pro, Edge, and Volt
Requirements: MEA Creator Kit

Coffee Break Webinars
Sit back with a cup of coffee and enjoy these 10-minute on-demand webinars.

The spectrum in a dish: Using neurophysiology to build a human iPSC model of autism
Maestro MEA,
optimized for organoids
Maestro MEA is powering the future of organoid research. From real-time functional insights to breakthrough 3D innovations, Maestro is the MEA system built for organoids.
Neural Organoid Publications
Browse over 85 selected publications illustrating how scientists around the world are using neural organoids for disease research and therapeutic discovery.
Disease research
16p11.2 disorders
ALS
- >> Biosensing system for drug evaluation of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis based on muscle bundle and nano-biohybrid hydrogel composed of multiple motor neuron spheroids and carbon nanotubes
- >> Neuromuscular organoids model spinal neuromuscular pathologies in C9orf72 amyotrophic lateral sclerosis
Alzheimer’s disease
- >> Modeling Sporadic Alzheimer’s Disease in Human Brain Organoids under Serum Exposure
- >> Mechanisms of hyperexcitability in Alzheimer's disease hiPSC-derived neurons and cerebral organoids vs. isogenic controls
- >> NitroSynapsin ameliorates hypersynchronous neural network activity in Alzheimer hiPSC models
Autism spectrum disorders
- >> Dysregulation of miRNA expression and excitation in MEF2C autism patient hiPSC-neurons and cerebral organoids
- >> Transcription Factor 4 loss-of-function is associated with deficits in progenitor proliferation and cortical neuron content
- >> Human forebrain organoids reveal connections between valproic acid exposure and autism risk
Congenital central hypoventilation syndrome (CCHS)
Focal cortical dysplasia
- >> Junctional instability in neuroepithelium and network hyperexcitability in a focal cortical dysplasia human model
- >> Personalized Human Astrocyte-Derived Region-Specific Forebrain Organoids Recapitulate Endogenous Pathological Features of Focal Cortical Dysplasia
Glioblastoma
- >> Electrophysiological characterization of glioma using a biomimetic Spheroid Model
- >> Glioblastoma remodelling of human neural circuits decreases survival
- >> Modeling the precise interaction of glioblastoma with human brain region-specific organoids
Hypothalamus disorders
Lewy body diseases
Myasthenia gravis (NMJ)
Noonan syndrome
Optogenetics
PACS1 syndrome
Pain
- >> Human Spinal Organoid-on-a-Chip to Model Nociceptive Circuitry for Pain Therapeutics Discovery
- >> Generation of human region-specific brain organoids with medullary spinal trigeminal nuclei
Parkinson's Disease
- >> 𝜶-Synuclein Pathology Spreads in a Midbrain–Hindbrain Assembloid Model
- >> Impaired neuron differentiation in GBA-associated Parkinson’s disease is linked to cell cycle defects in organoids
- >> Insulin resistance compromises midbrain organoid neuronal activity and metabolic efficiency predisposing to Parkinson’s disease pathology
- >> Unraveling the assembloid: Real-time monitoring of dopaminergic neurites in an inter-organoid pathway connecting midbrain and striatal regions
Prader-Willi
Retinoblastoma
Rett syndrome
Schizophrenia
- >> Human forebrain organoid-based multi-omics analyses of PCCB as a schizophrenia associated gene linked to GABAergic pathways
- >> miRNA profiling of hiPSC-derived neurons from monozygotic twins discordant for schizophrenia
Viral infection
- >> Acetate, a metabolic product of Heligmosomoides polygyrus, facilitates intestinal epithelial barrier breakdown in a FFAR2-dependent manner
- >> Brain organoids-on-chip for neural diseases modeling: History, challenges and trends
- >> Host Plasma Microenvironment in Immunometabolically Impaired HIV Infection Leads to Dysregulated Monocyte Function and Synaptic Transmission Ex Vivo
- >> Modeling Human Cytomegalovirus-Induced Microcephaly in Human iPSC-Derived Brain Organoids
- >> Neurodegeneration in human brain organoids infected with herpes simplex virus type 1
Neurodevelopment and neurodegeneration
- >> A Robust Pipeline for the Multi-Stage Accelerated Differentiation of Functional 3D Cortical Organoids from Human Pluripotent Stem Cells
- >> Buprenorphine and methadone differentially alter early brain development in human cortical organoids
- >> CB1 antagonism increases excitatory synaptogenesis in a cortical spheroid model of fetal brain development
- >> Complex oscillatory waves emerging from cortical organoids model early human brain network development
- >> Developmental GABA polarity switch and neuronal plasticity in Bioengineered Neuronal Organoids
- >> Human cerebral spheroids undergo 4 aminopyridine induced, activity associated changes in cellular composition and microRNA expression
- >> Hyaluronan regulates synapse formation and function in developing neural networks
- >> Loss of GTF2I promotes neuronal apoptosis and synaptic reduction in human cellular models of neurodevelopment
- >> Natural variation in gene expression and viral susceptibility revealed by neural progenitor cell villages
- >> Neurodevelopmental defects in human cortical organoids with N-acetylneuraminic acid synthase mutation
- >> Proteasome stress in skeletal muscle mounts a long-range protective response that delays retinal and brain aging
- >> Reintroduction of the archaic variant of NOVA1 in cortical organoids alters neurodevelopment
- >> The Role of KDM2A and H3K36me2 Demethylation in Modulating MAPK Signaling During Neurodevelopment
Neurotoxicology
- >> Evaluation of Neurotoxicity With Human Pluripotent Stem Cell–Derived Cerebral Organoids
- >> Impact of alcohol exposure on neural development and network formation in human cortical organoids
- >> Methadone interrupts neural growth and function in human cortical organoids
- >> Molecular and Functional Characterization of Different BrainSphere Models for Use in Neurotoxicity Testing on Microelectrode Arrays
- >> Multi-organ model assessment of neurotoxicity following exposure of liver spheroids to drugs
- >> Generation of neural organoids for spinal-cord regeneration via the direct reprogramming of human astrocytes
- >> Sensor Technologies for Quality Control in Engineered Tissue Manufacturing
- >> Adoption of microfluidic MEA technology for electrophysiology of 3D neuronal networks exposed to suborbital conditions
- >> Antidepressant aripiprazole induces adverse effects on neural development during cortex organoid generation
- >> A versatile polypharmacology platform promotes cytoprotection and viability of human pluripotent and differentiated cells
- >> Effects of microgravity on human iPSC-derived neural organoids on the International Space Station
- >> Effective cryopreservation of human brain tissue and neural organoids
- >> Establishing Neural Organoid Cultures for Investigating the Effects of Microgravity in Low-Earth Orbit (LEO)
- >> Generation of human iPSCs derived heart organoids structurally and functionally similar to heart
- >> Generation of self-organized neuromusculoskeletal tri-tissue organoids from human pluripotent stem cells
- >> Generation of ‘semi-guided’ cortical organoids with complex neural oscillations
- >> High-throughput screening of human induced pluripotent stem cell-derived brain organoids
- >> Human apical-out nasal organoids reveal an essential role of matrix metalloproteinases in airway epithelial differentiation
- >> Human microglia states are conserved across experimental models and regulate neural stem cell responses in chimeric organoids
- >> [PRE-PRINT] Microglia integration into human midbrain organoids leads to increased neuronal maturation and functionality. (update-published in Glia)
- >> Molecularly cleavable bioinks facilitate high-performance digital light processing-based bioprinting of functional volumetric soft tissues
- >> Quantitative and Qualitative Analysis of Neurotransmitter and Neurosteroid Production in Cerebral Organoids during Differentiation
- >> Synergistic hyperactivation of both mTORC1 and mTORC2 underlies the neural abnormalities of PTEN-deficient human neurons and cortical organoids
- >> Three-dimensional liquid metal-based neuro-interfaces for human hippocampal organoids
- >> Vascular network-inspired diffusible scaffolds for engineering functional midbrain organoids
Regenerative medicine
Organoid development and optimization
Neural Organoid Application Notes and Culture Protocols
Learn how easy it is to monitor neural organoids on Axion's hands-free, automated platforms.
Discover how Axion’s next-generation live-cell analysis tools can accelerate your disease research and drug discovery workflows:
>> Maestro multielectrode array (MEA) platform — Assess key parameters of neural network function in real time with Axion’s nonstop, noninvasive, label-free Maestro MEA and powerful, intuitive software.
>> Omni imaging platform — Visualize the growth, differentiation, cell morphology, and cell viability of neural organoids as they develop with Axion’s automated, AI-supported live-cell imaging tools.