
Lumos MEA Plate
Axion BioSystems Lumos multiwell microelectrode array (MEA)™ plates combine high quality MEA results with highly optimized optical performance.
Available in 24-, 48-, and 96- well options, the custom-built Lumos lid and specially formulated plate walls have been optimized to maximize light delivery to your cell culture and minimize well-to-well cross-talk. The transparent well bottoms allow for cell visualization and assay multiplexing with fluorescence, luminescence, and other reporter-based assays.
Key Features
High throughput optical control.
>> High throughput, multiwell format
Lumos MEA microelectrode array (MEA) plates provide high-quality results.
>> Optimal light delivery and dispersion
Customized plate material and lid optics enhance light delivery and allow for even light dispersion.
>> Multiplex your assay
Use Axion's Lumos™ system to perform optogenetic experiment to complement your MEA data.
Lumos MEAThe Lumos MEA plates combine robustness and assay flexibility of a CytoView MEA plate with white walls and a custom optical lid for optimal light delivery in each well | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Plate | Cat No. | Wells | Electrode/ | Electrode | Bottom | Walls | Maestro Volt | Maestro | Maestro | Maestro | Maestro |
| Lumos MEA 24 | M384-tMEA-24OPT | 24 | 16 PEDOT |  | Transparent | White | ● | ● | |||
| Lumos MEA 48 | M768-tMEA-48OPT | 48 | 16 PEDOT |  | Transparent | White | ● | ● | |||
| Lumos MEA 96 | M768-tMEA-96OPT | 96 | 8 PEDOT |  | Transparent | White | ● | ||||
*Schematic of well illustrating recording electrodes (blue), grounds (orange), and where present, a large dedicated stimulation (blue).
Overview
Cell visualization and assay multiplexing
The innovative, transparent plate bottom offers additional assay flexibility including cell visualization and assay multiplexing. Bright field imaging enables confirmation of cell spotting accuracy and correlation of cell culture health and connectivity with MEA results. Multiplex fluorescence- or luminescence-based assays with your MEA study to probe complementary end points.
Optogenetics to control the pacing or bursting of your cells
Genetically modification of cells to express excitatory light-sensitive ion channels, such as channel rhodopsin (ChR2), allows for controlled pacing of cardiomyocyte beating or neural network bursting.
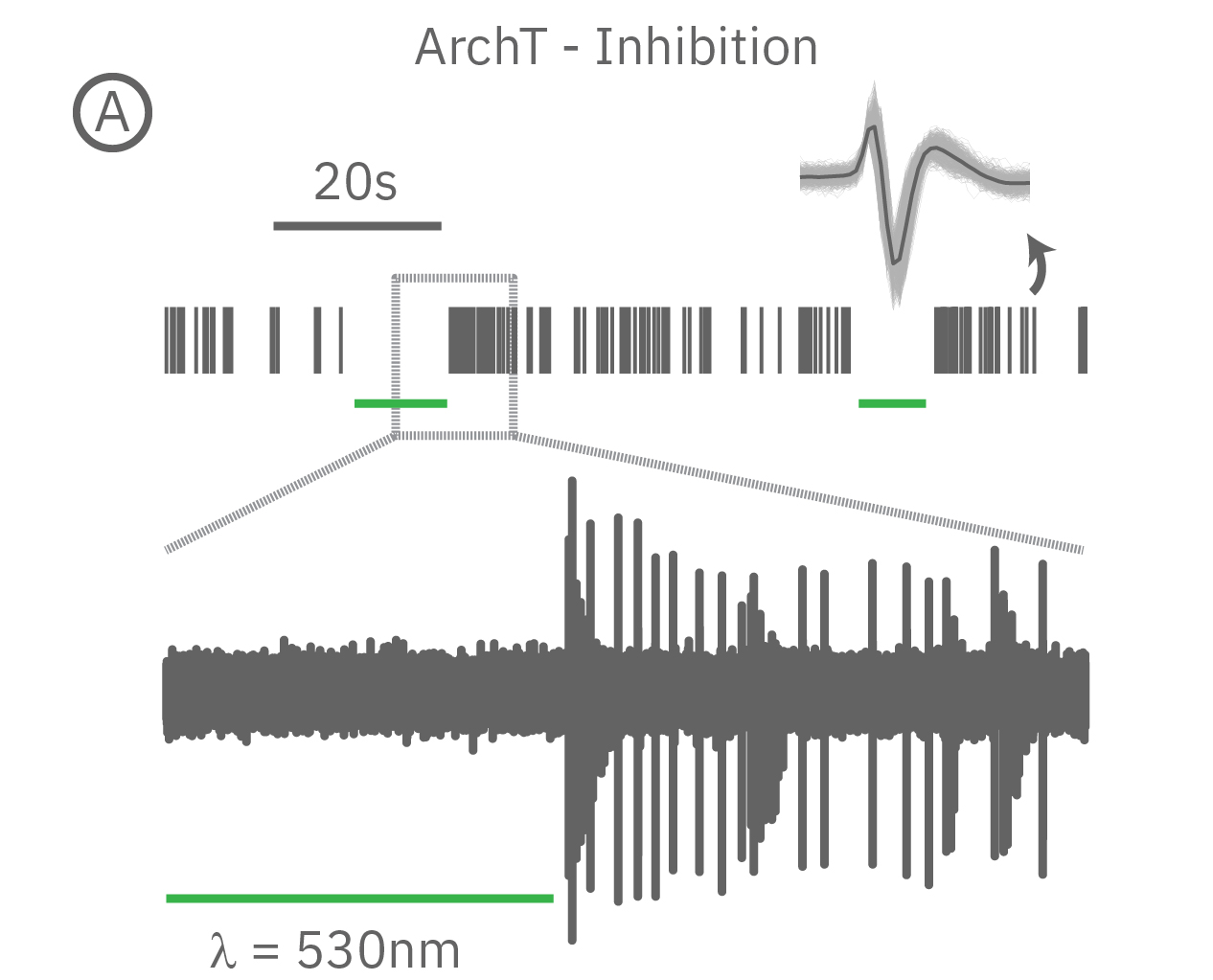
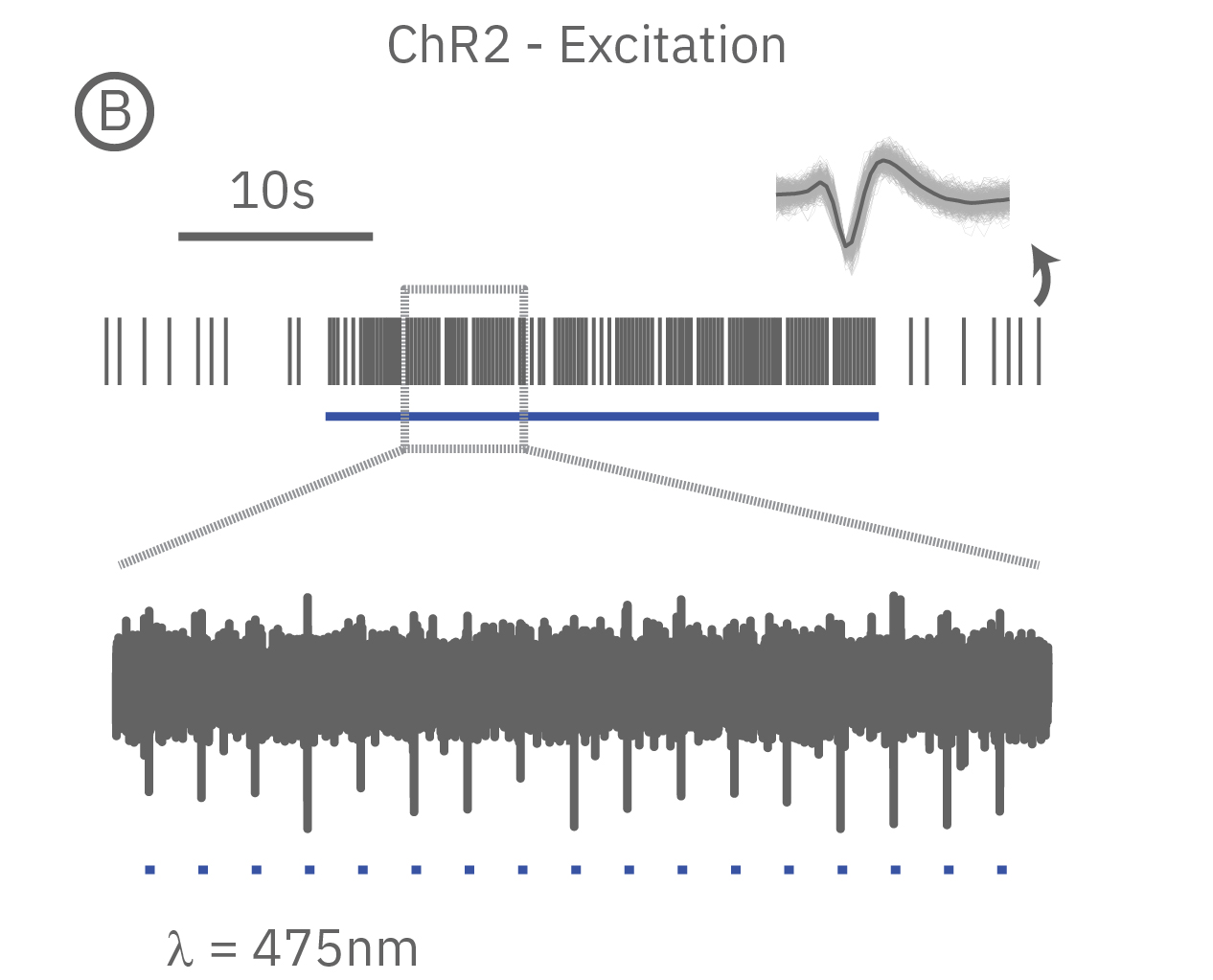
(A) When expressed in neurons, ArchT suppresses neural activity upon incident green light. (B) Whereas, ChR2 can be used to activate neurons in vitro in response to blue light.
For cardiomyocytes, cardiac repolarization is intrinsically linked to the beat frequency, both of which are sensitive to pharmacological manipulation. Optogenetic stimulation can be used to control the beat frequency and remove it as a variable, resulting in increased reliability of the repolarization measurement.
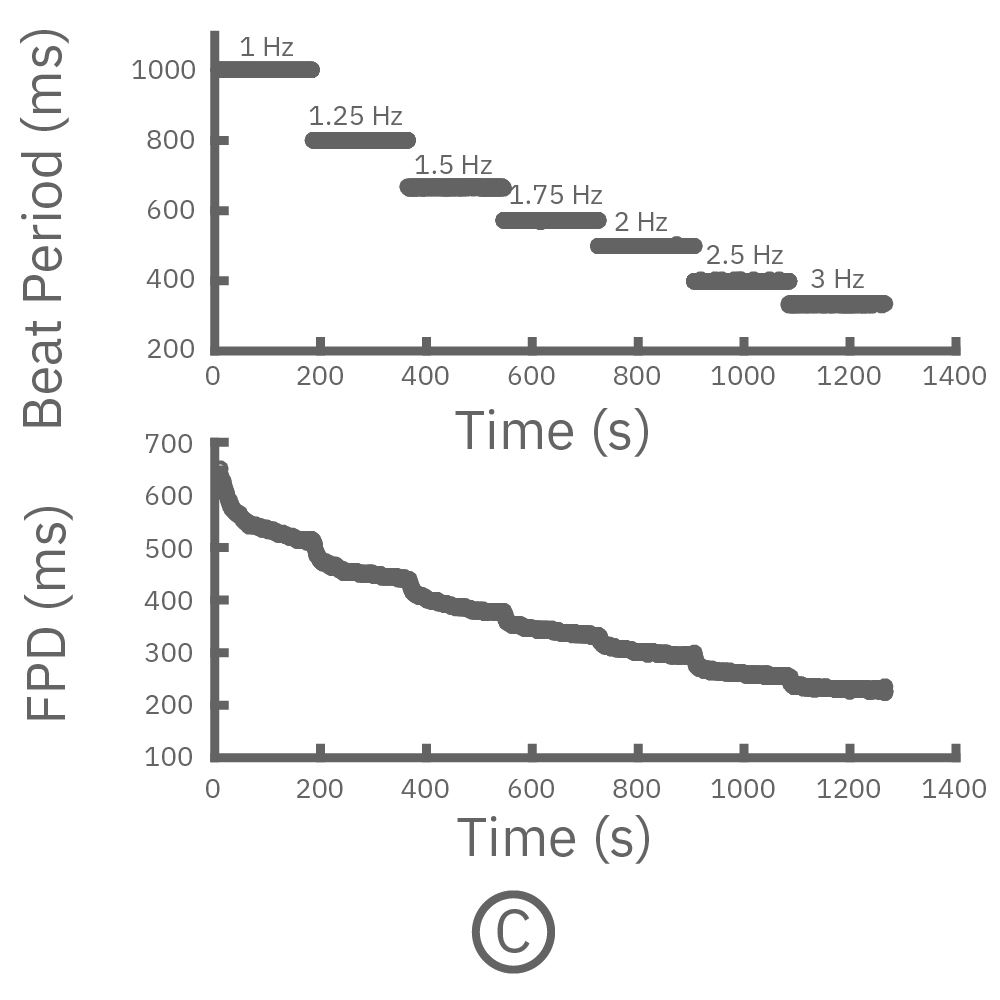
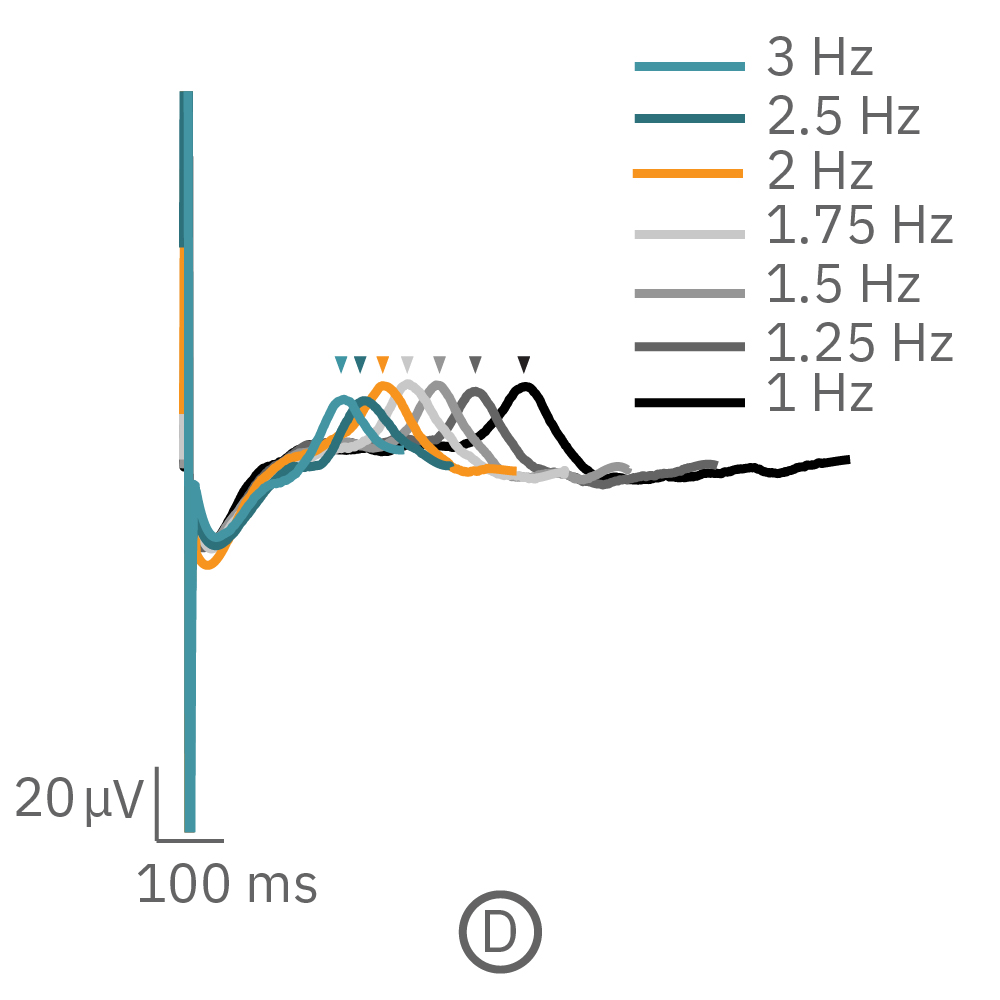
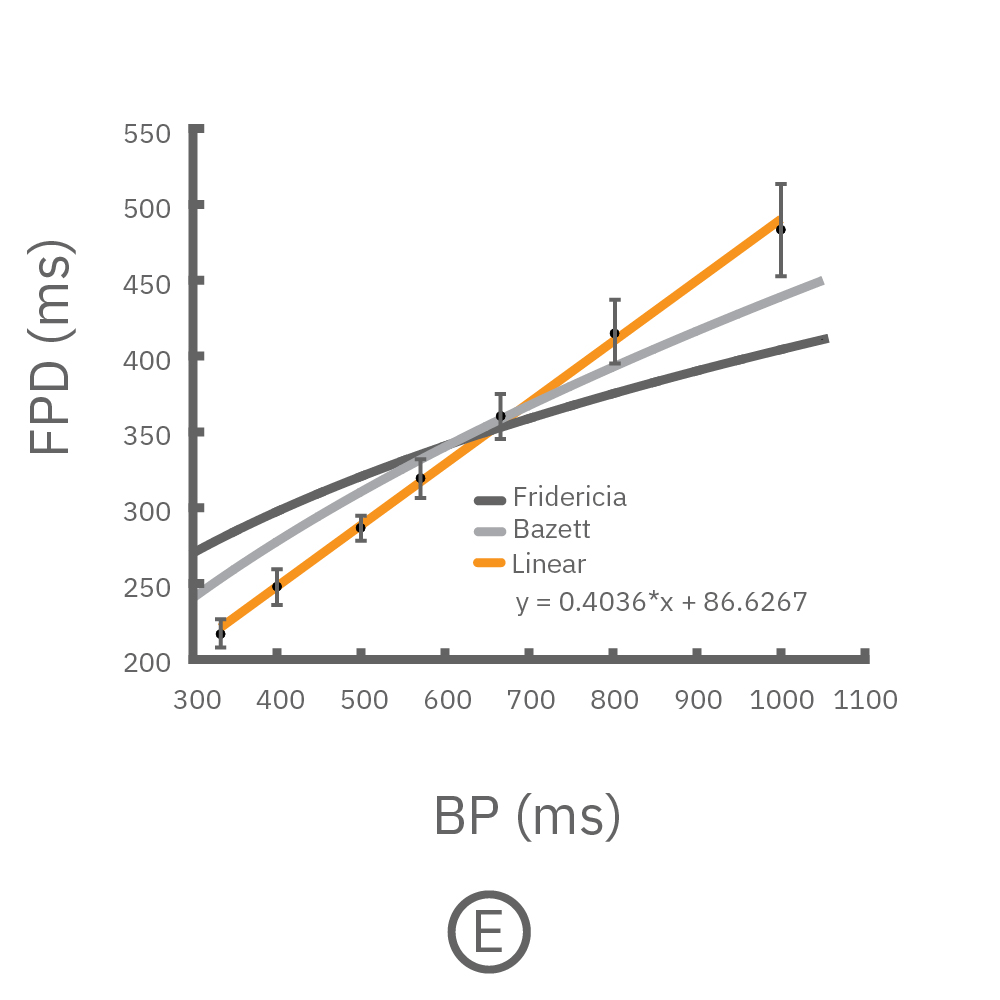
(C, D) The beat rate of Pluricyte® Cardiomyocytes was increased in a step-wise manner (known as a “chirp” assay). The field potential duration (FPD) adapted with each sequential beat rate increase up to 3 Hz. (E) Typical clinical correction formulas, the Fridericia and Bazzett, did not accurately predict the FPD. However, pacing with the Lumos revealed the cell-specific beat rate correction relationship.