What is Live-Cell Imaging?
Live-cell imaging uses microscopy to analyze the structure, behavior, and organization of living cells in real time. Live-cell imaging captures dynamic, time-dependent cellular processes that are easily missed if analyzed using traditional endpoint methods limited to a single time point. This aids in the development of more biologically relevant and accurate in vitro assays. Live-cell imaging covers a wide range of applications, including the analysis of cell health and proliferation, cell migration, morphology, and function.

Live-Cell Imaging Workflows
Live-cell imaging and analysis can be integrated at multiple stages of an experimental workflow, including initial assay optimization, assay execution, and data interpretation.
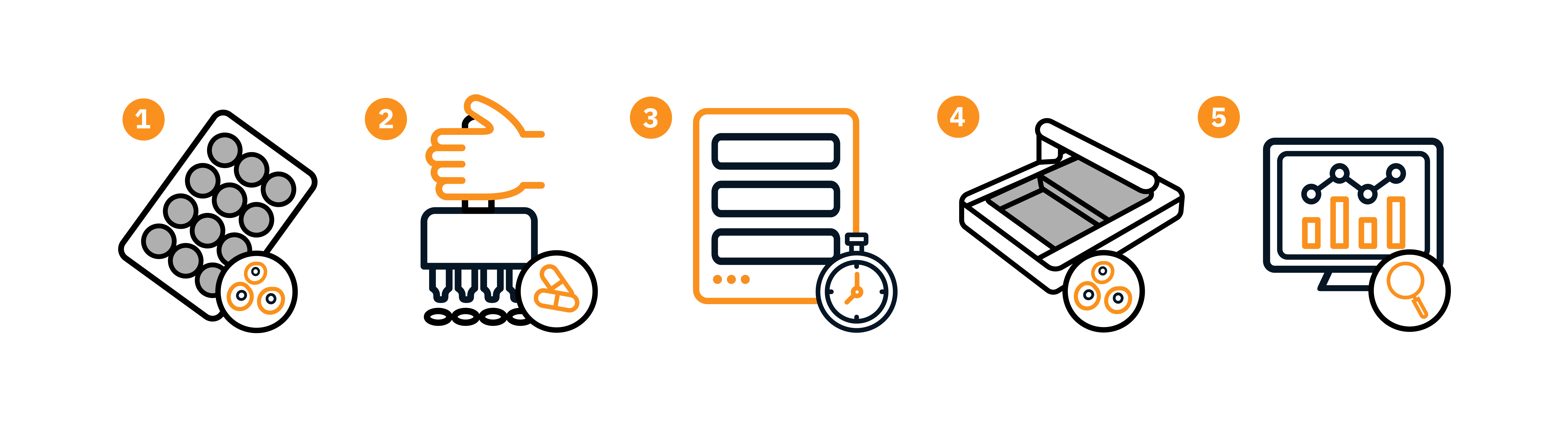
A generalized workflow for live-cell imaging assays will typically involve the following steps:
- 1. Cell preparation – cells are plated into labware of choice (well plate, T-flask, petri dish, microfluidic chips).
- 2. Cell treatment – if applicable, necessary cell treatments are performed.
- 3. Incubation – the culture dish is then placed on an automated live-cell imaging system; if the system operates inside an incubator, then full environmental control is enabled, including temperature, humidity, and CO2 levels.
- 4. Image acquisition – live-cell images are acquired at regular intervals over a specified time period.
- 5. Data analysis – quantitative analysis of live-cell imaging data using image analysis software.
Advantages of Live-Cell Imaging
Live-cell imaging has revolutionized cell biology research, as it offers unique advantages compared to traditional endpoint assays and methods of cell analysis. The key advantages of live-cell imaging include:
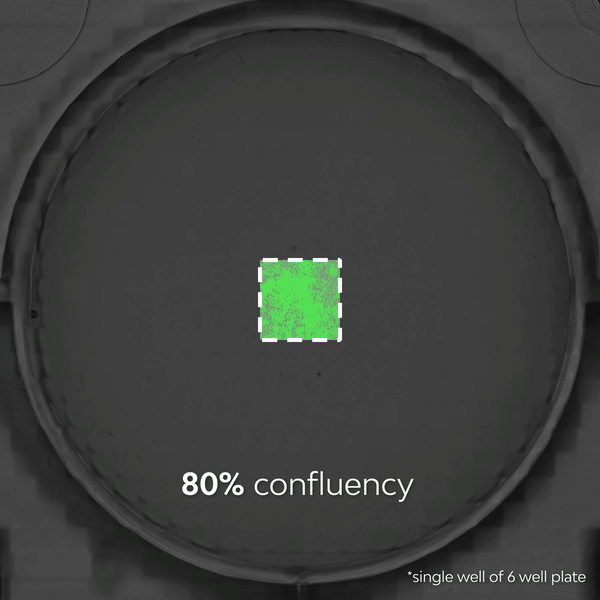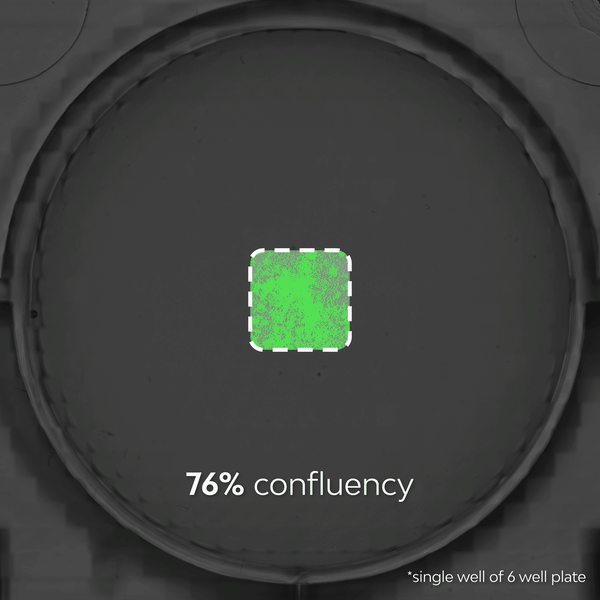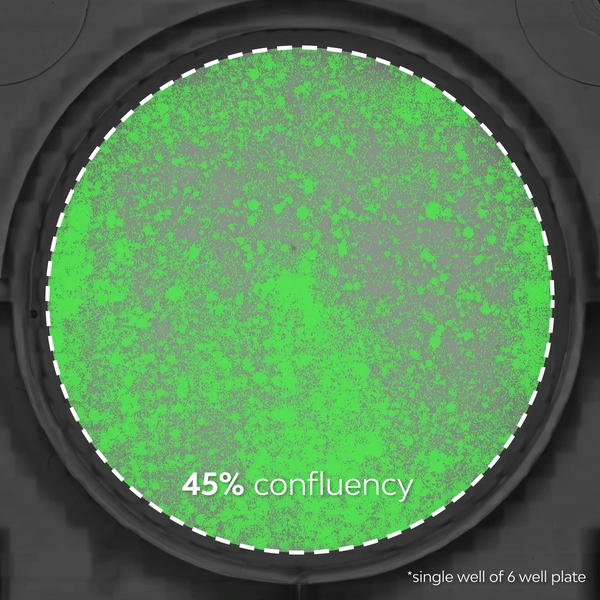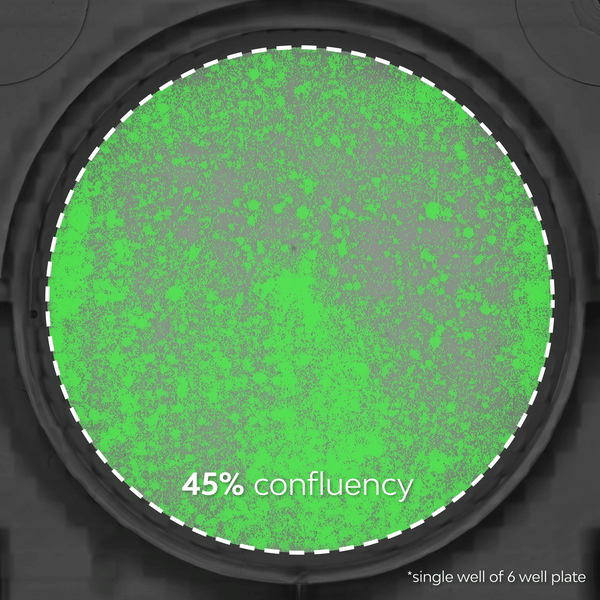
- >> Observe dynamic biological processes – Live-cell imaging shows cellular processes as they occur in real time, providing insights into dynamic, transient events such as cell division, migration, and signaling as they happen and allowing researchers to quantify detailed kinetic metrics.
- >> Preserve native cellular environment – Live-cell imaging can be performed in controlled environmental conditions to maintain cells in their native physiological state, minimizing artifacts and ensuring the biological relevance of assays.
- >> Combine brightfield and fluorescence imaging – While each imaging modality offers a unique set of advantages, the combination of kinetic brightfield imaging with fluorescence microscopy enables a comprehensive investigation into dynamic cellular behaviors.
- >> Assay a multitude of cell types and processes – Live-cell imaging can be adapted to study a wide range of biological processes and cell types, ranging from cell proliferation to immune cell killing and tumor organoid development.
Live-cell imaging lets researchers observe and study dynamic cellular events in real time and under physiological conditions, providing critical insights into the behavior, function, and interaction of different cells.
Live-Cell Imaging Analysis and AI
Live-cell imaging analysis involves extracting quantitative information from recorded live-cell microscopy data, such as cell number, morphology, and movement. This analysis can be performed manually or with the help of specialized software that offers automated measurement, segmentation, and tracking tools. With advancements in artificial intelligence (AI), live-cell imaging analysis can utilize machine learning-based algorithms to mediate the extraction of information from live-cell imaging data.
AI-based live-cell imaging analysis is key for efficient and reproducible detection and quantification of kinetic cellular events, as it offers an unprecedented degree of accuracy, speed, and scalability. It can be used to automatically detect and count individual cells in a sample, examine cell morphology, characterize complex 3D cell cultures, such as spheroids and organoids, and quantify the progression of dynamic cellular events, including cell proliferation, migration, and invasion. In all these cases, capturing and measuring the kinetics of cellular behavior, offered by AI-driven live-cell imaging analysis, not only expands the capabilities of traditional in vitro assays, but also offers a wealth of information that is not as readily available when examined using a manual approach or a standard computerized method.

By harnessing the power of cloud computing, live-cell image analysis algorithms can rapidly and consistently process large volumes of data and efficiently extract information from images with background noise and artifacts. In addition, cloud-based platforms offer scalability of storage, enabling researchers to securely store and manage massive datasets without concerns about storage limitations.
Whole-well live-cell imaging analysis of collective glioma cell migration. After stitching together numerous images taken over the entire well, AI algorithms automatically quantifies the gap (blue) closure and cell migration speed with a high degree of spatial and temporal resolution.
Choosing a Live-Cell Imaging System
With different live-cell imaging systems and options on the market, it is important to know what features are needed for your research. Here are some key considerations for evaluating live-cell imaging systems:
- >> What imaging configurations do you need for your experiment? Brightfield is often ideal for long-term assays, having the benefit of being label-free. Fluorescent capabilities can add assay flexibility but require balancing additional channels with additional cost. Variability based on sample size is influenced by number of images taken per well, but some systems feature whole-well imaging, reducing variability due to limited sampling.
- >> What are your throughput requirements?There are live-cell systems capable of taking single site images, imaging each well of an entire plate, or handling multiple plates at once. Understanding your lab’s usage can help in determining the right system. For multiplate systems, look for a system that makes scheduling easy among multiple users and options to share data and collaborate.
- >> Does the system have adequate environmental control? Maintaining temperature, humidity, and CO2 is crucial for maintaining physiological conditions for live-cell imaging over time. Some live-cell imaging systems solve this issue by operating within a cell culture incubator but look for a system with the right footprint and ask about excess heat generation.
- >> Are your culture vessels compatible? Not all live-cell imaging systems can measure from every plate. Some require specific plate definitions already loaded while others are more flexible. While often fine for standard multiwell plates, it may be too restrictive for custom microfluidic devices, less common plate formats, or even flasks.
- >> How user-friendly is the software and data management? Live-cell imaging systems can generate a lot of images which require adequate computational capabilities. A user-friendly analysis software suitable for your experimental needs will help you get the most from your live-cell imaging analysis. With large files and datasets, data storage can often be a hidden cost, but newer live-cell imaging systems offer cloud-based solutions that are more affordable, computationally faster, and can grow with your needs better than in-house solutions.
Live-Cell Imaging Systems
Axion BioSystem’s Omni and Lux live-cell imaging platforms come with a variety of options and throughput to meet the needs of any academic, pharmaceutical, or biotechnology lab. By considering these factors, your lab can find the right live-cell imaging system for your research.

Live-Cell Imaging Applications
Live-cell imaging is a versatile tool that can be adapted to study a wide range of biological processes and cell types in vitro, from standard 2D cell cultures to complex multicellular organoids, offering versatility in experimental design and application.