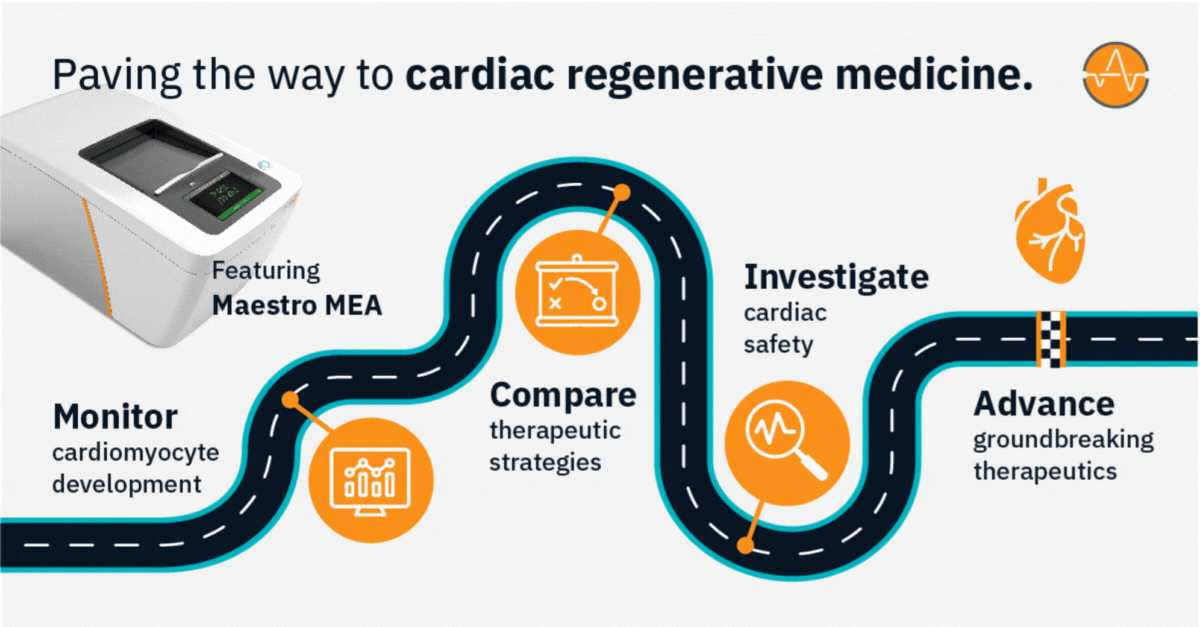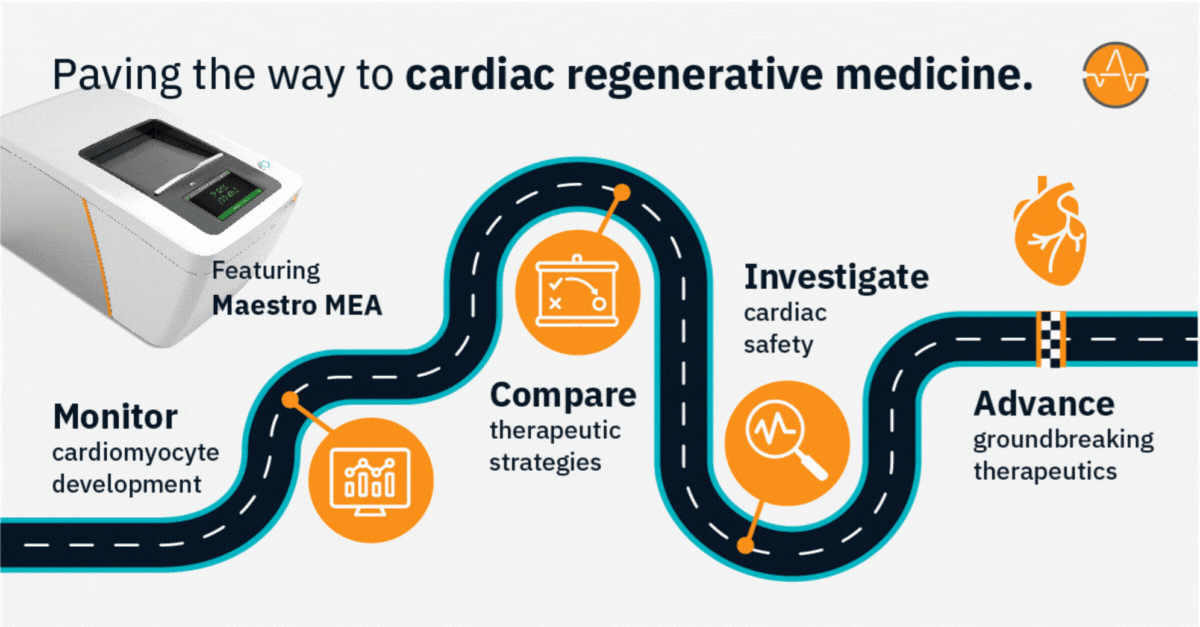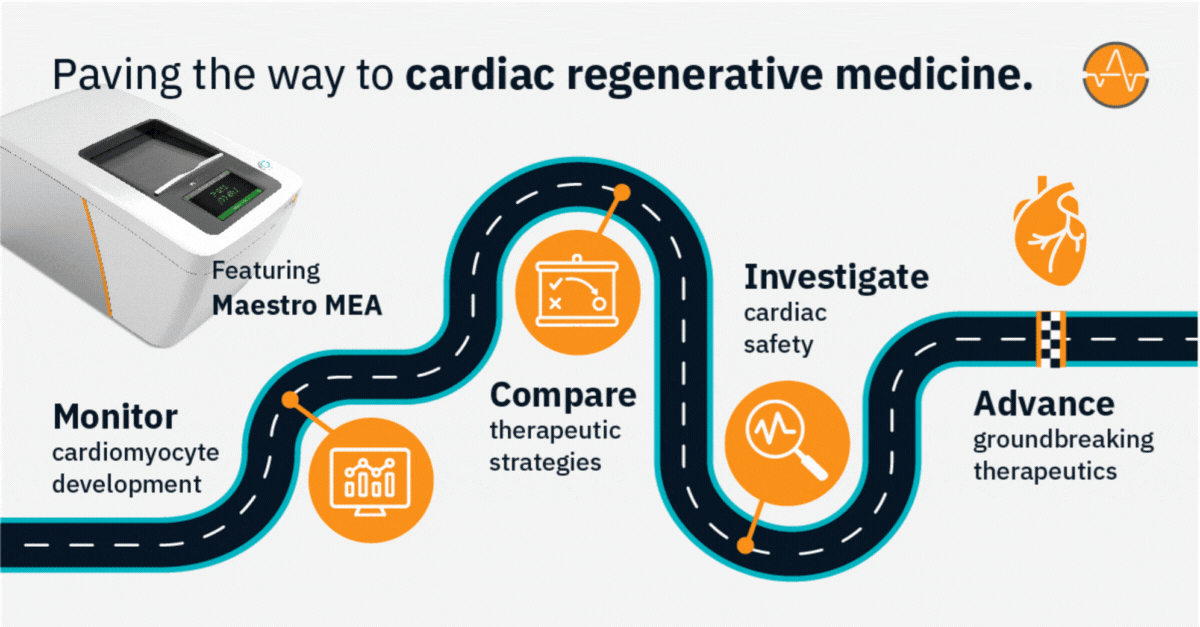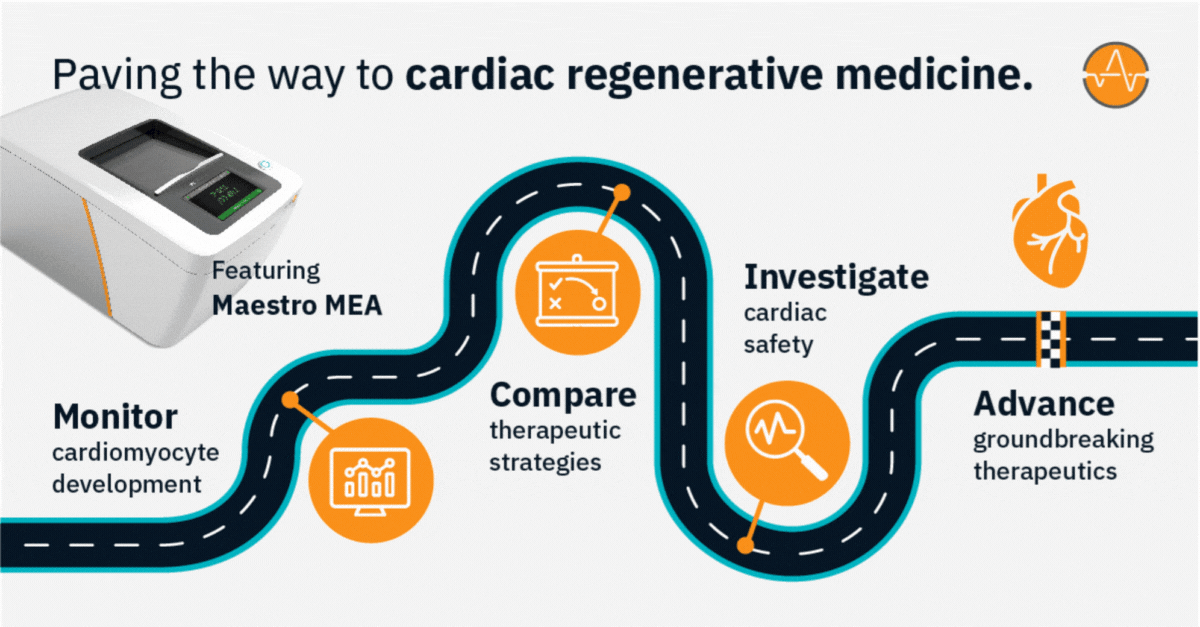
Pave the way to cardiac regenerative medicine
Cardiac regenerative medicine aims to restore or replace damaged heart tissue in an effort to improve heart function and treat cardiovascular conditions. With clinical trials currently evaluating regenerative medicine strategies for post-myocardial infarction heart failure and coronary artery disease, experts expect these groundbreaking therapies may soon advance from bench to bedside.
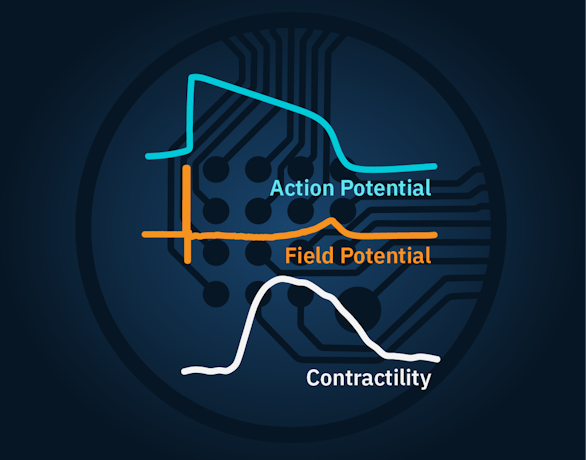
Axion’s versatile live-cell analysis systems offer a powerful platform for studying cardiac regeneration in 2D and 3D cell cultures in vitro—in real time with no labels, dyes, or complicated steps.
>> Track the differentiation and maturation of cardiomyocytes over days, weeks, or months
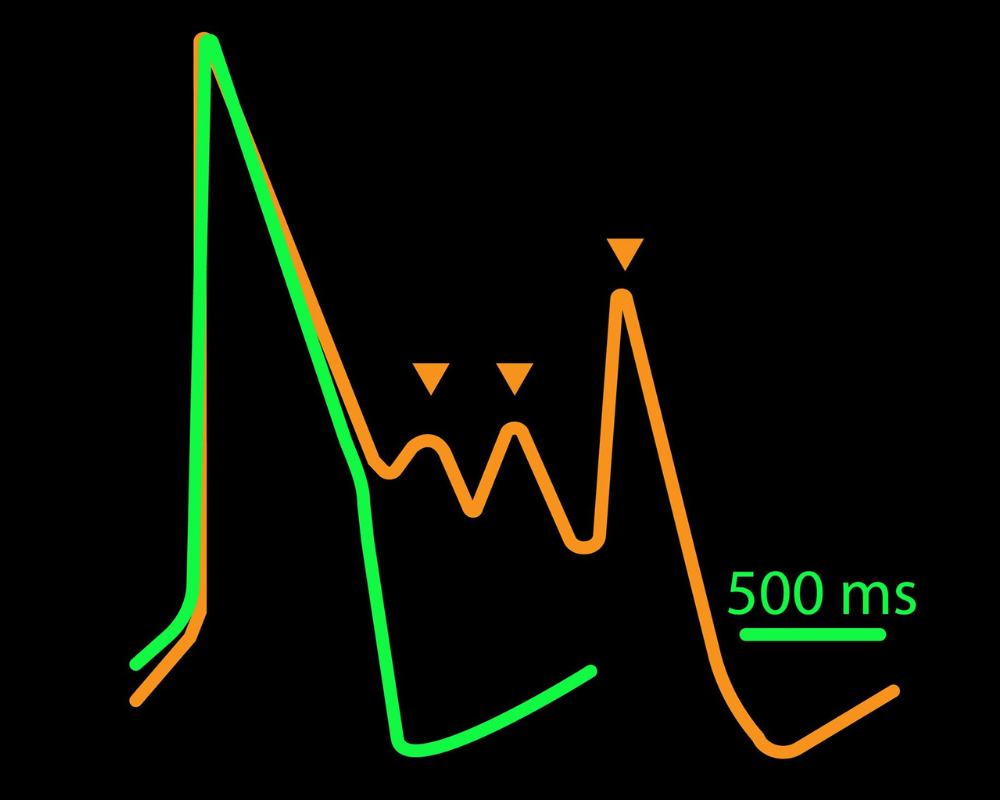
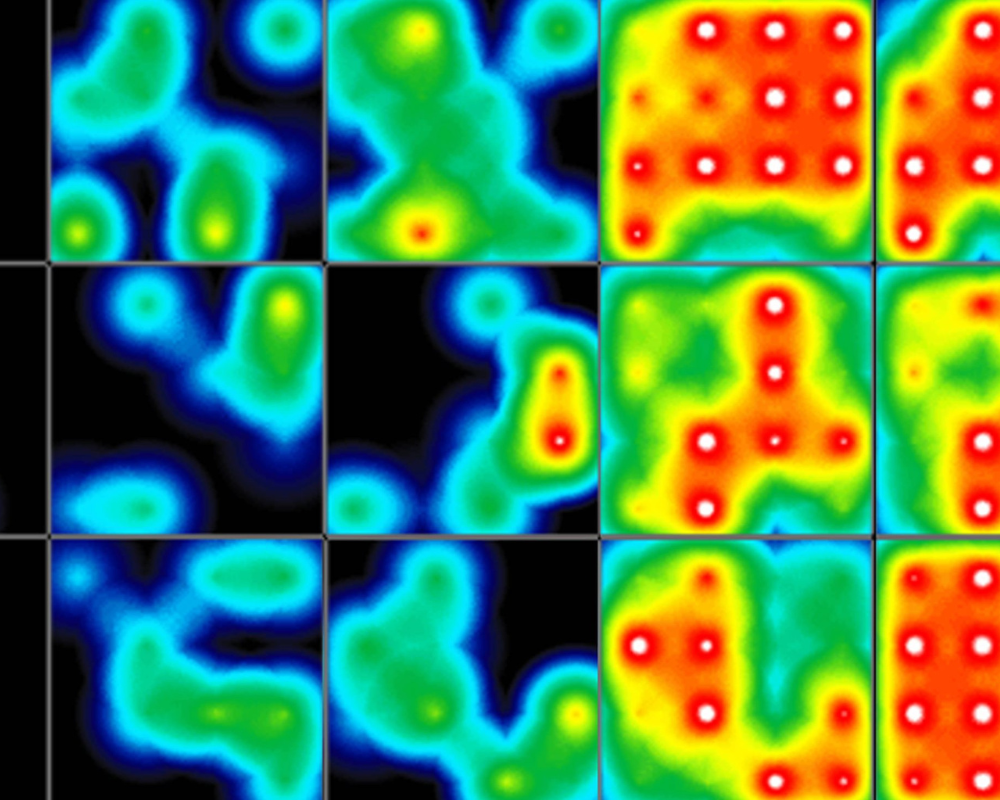
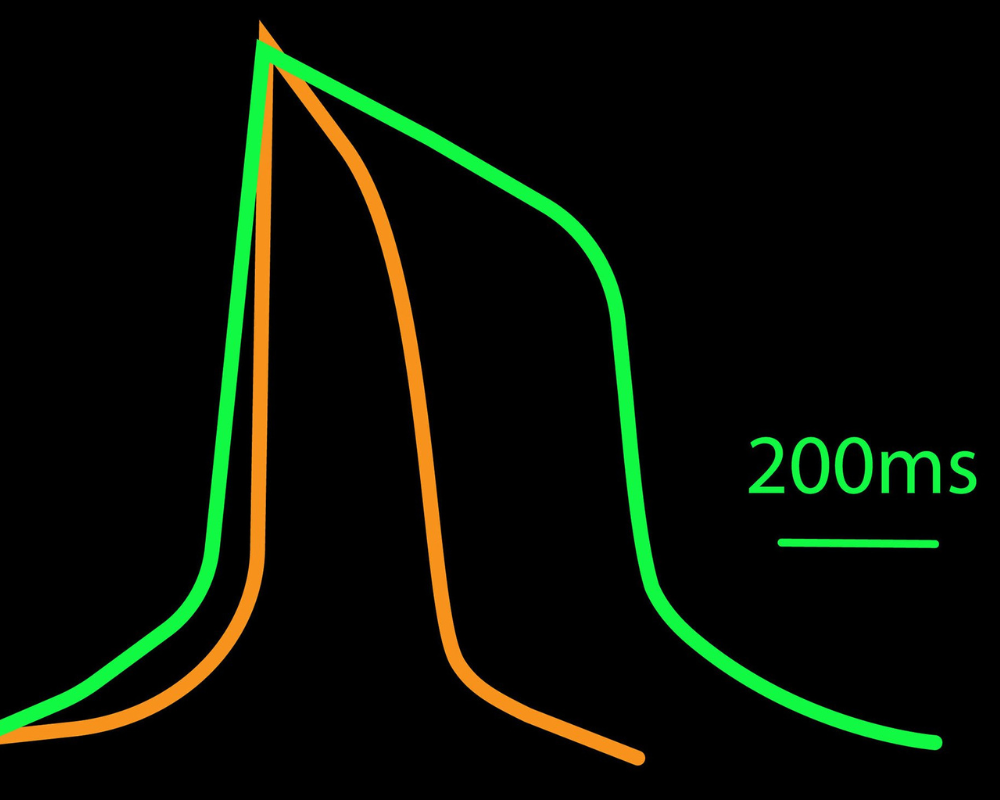
>> Assess key parameters of cardiac action potentials, contraction, and propagation in real time
>> Investigate mechanisms of cardiac disease and regeneration without disturbing your cells
>> Evaluate the functional effects of therapeutic strategies for repairing damaged heart tissue

Featured cardiac research publications
Read selected publications to learn how scientists are using Axion’s MEA platform to advance cardiac regenerative medicine research.
>> Gene editing to prevent ventricular arrhythmias associated with cardiomyocyte cell therapy
Maestro Pro: The premiere bioelectronic assay system
The Maestro Pro can do it all. Compatible with all modules and plate types, the Maestro Pro features maximum flexibility and throughput. Take electrophysiology to the next level with detailed analysis and up to 96 wells assayed simultaneously.
Cardiac Applications
Speak to a specialist
What is cardiac regenerative medicine? >>
Therapeutic strategies designed to repair heart damage from myocardial infarction and other cardiovascular conditions are advancing at a rapid pace, potentially putting the promise of cardiac regeneration within reach. Scientists are exploring a number of cardiac regenerative medicine approaches in the lab and in human clinical trials.
>> Stem cell therapy: Scientists are investigating the use of embryonic stem cells, induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs), and adult stem cells (e.g., mesenchymal stem cells), to regenerate damaged heart tissue. The cells are delivered directly to the heart through injections or implanted using tissue‑engineered constructs
>> Gene therapy: Gene therapy involves introducing specific genes into the heart tissue to promote cell growth, differentiation, and regeneration. This approach aims to modify the genetic makeup of cardiac cells to enhance their regenerative capacity.
>> Tissue engineering: Scientists use biomaterials, scaffolds, and cells to build tissue‑engineered constructs that can be transplanted into the heart to promote tissue regeneration and improve cardiac function.
>> Cardiac patch therapy: Cardiac patches are thin, cell‑seeded biomaterial sheets designed to repair damaged areas of the heart. These patches can be applied surgically to provide structural support and deliver therapeutic cells to the injured site, facilitating tissue repair.
>> Exosome therapy: Exosomes are small vesicles released by cells that contain various signaling molecules, including proteins and microRNAs. Researchers are exploring the potential of using exosomes derived from stem cells or other cell types to stimulate cardiac repair and regeneration.
>> Bioactive molecules and growth factors: Certain molecules and growth factors can promote cell proliferation, angiogenesis (formation of new blood vessels), and tissue repair. Delivering these bioactive agents directly to the heart can enhance its regenerative capacity.