Cell Culture Protocol
FCDI iCell GlutaNeurons
Preparing the MEA Plate
- Add 50 μl of 0.1% PEI solution to each well in the MEA plate.
Recommended to add 6-8 mL of sterile water to the on-plate reservoirs to increase humidity.
- Incubate the PEI-coated MEA plate in a cell culture incubator at 37°C, 5% CO2 for at least 60 minutes.
- Rinse PEI from the culture surface with 200 µl of sterile DI water 4 times, then allow the MEA plate to air dry overnight.
Culturing iCell GlutaNeurons
- Prepare iCell GlutaNeuron media according to the FCDI iCell GlutaNeuron User’s Guide. Aliquot media in functional 10-15 ml aliquots, store at -80°C, and thaw at room temperature as needed. Laminin should be added to freshly thawed media as per User Guide recommended concentration.
Prepare the laminin fresh from frozen aliquots for every cell culture.
- Thaw iCell GlutaNeurons according to the FCDI iCell GlutaNeuron User’s Guide.
- Remove a sample of the cell suspension and count the neurons using a hemocytometer to determine both the viability and total number of viable cells. Transfer the cell suspension to a 15 ml conical tube.
Ensure the neurons are evenly suspended before removing an aliquot to count.
- Centrifuge the cell suspension at 180 x g for 5 minutes.
Neurons are sensitive to centrifugation, so care should be taken to monitor speed and duration during this step. The cell provider does not recommend centrifugation and is not responsible for cell death induced by centrifugation.
- Aspirate the supernatant, being careful not to disturb the cell pellet.
- Dilute the cell suspension in complete medium combined with laminin (20µg/ml) to 12,000,000 neurons/ml.
Plating iCell GlutaNeurons onto the MEA
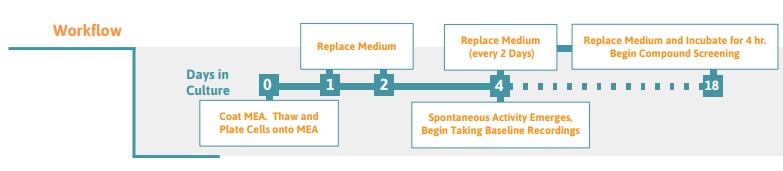
- Place a 10 µl droplet of iCell GlutaNeuron suspension over the recording electrode area of each well of the MEA. See Figure 1 on page 2 for appropriate drop placement.
- Incubate the MEA plate with the seeded neurons in a cell culture incubator at 37°C, 5% CO2 for 1 hour.
- Gently add 1/2 of the final volume of the medium to each well of the MEA. Adding the medium too quickly will dislodge the adhered neurons. Recommended final well volumes for each plate type are: 6- and 12-well = 1000 µl, 24-well = 500 µl, 48-well = 300 µl, 96 well = 200 µl.
Using a pipettor, add medium first in a semi-circle along the outer edge of the well. Progressively add medium to either side of the well so it fills evenly towards the center. The goal is to prevent a rush of medium in either direction that might dislodge the neurons.
- Repeat step 12 a second time to reach the final recommended volume of medium.
- Incubate in a cell culture incubator at 37°C, 5% CO2.
- For optimal cell health, exchange 50% of the media on day 1 and 2 post-plating, then every 2 days after that. Though neural spikes may be detectable within 4 days, optimal neural network structure is typically achieved after 18 days in culture.
Drop Placement
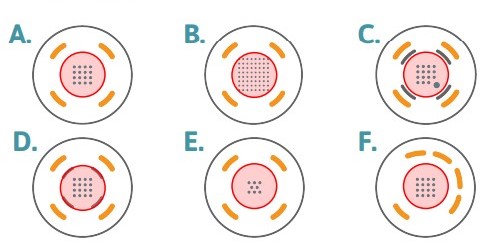
Figure 1: Drop Placement Diagram:
The layouts above represent the bottom surfaces of wells in (A) a 48-well MEA, (B) a 6- or 12-well MEA, (C) a 24-well MEA or 48 well E-Stim+ MEA, (D) a 48-well AccuSpot MEA, (E) a 96-well MEA, and (F) a 48-well CytoView MEA. The number of electrodes per well is different across the plate formats, however the drop placement is the same, with the drop (red circle) centered on the recording electrodes and staying within the ground electrodes. On plate types with the addition of the stim-paddle in the lower right corner of the array, it is important to make sure the droplet covers this feature. The droplet may need to be manipulated after placement of the pre-treatment to ensure stim-paddle coverage.
Visualization of Typical Neuron Seeding Results
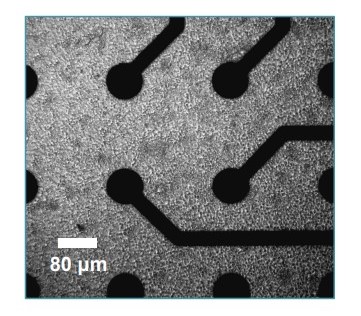
Figure 2: iCell Gluta Neuron Morphology:
iCell Gluta Neurons at day 1 in vitro in a 24-well CytoView MEA, 10x magnification. Notice that neuron morphology is easily recognizable.
Required Materials