神経毒性は、ある物質によって正常な脳機能が改変されることにより発生し、発作、認知機能の低下、運動機能の低下、異常行動などの症状で現れます。典型的な細胞毒性試験である細胞死の測定は比較的簡単ですが、細胞死に至らない脳機能の低下を評価することは困難です。
Maestro MEA は、プレート上に埋め込まれた複数の微小電極を用いて神経細胞の電気的な活動を測定します。個々の神経細胞の発火の変化や、ネットワークレベルでの活動の変化を測定することにより、化合物による神経細胞機能の変化を評価することができます。
ラベルフリー、温度・CO2 濃度自動制御下の安定した試験は、化合物による急性的な変化のみならず、慢性的な評価、リスク予測にも適しています。
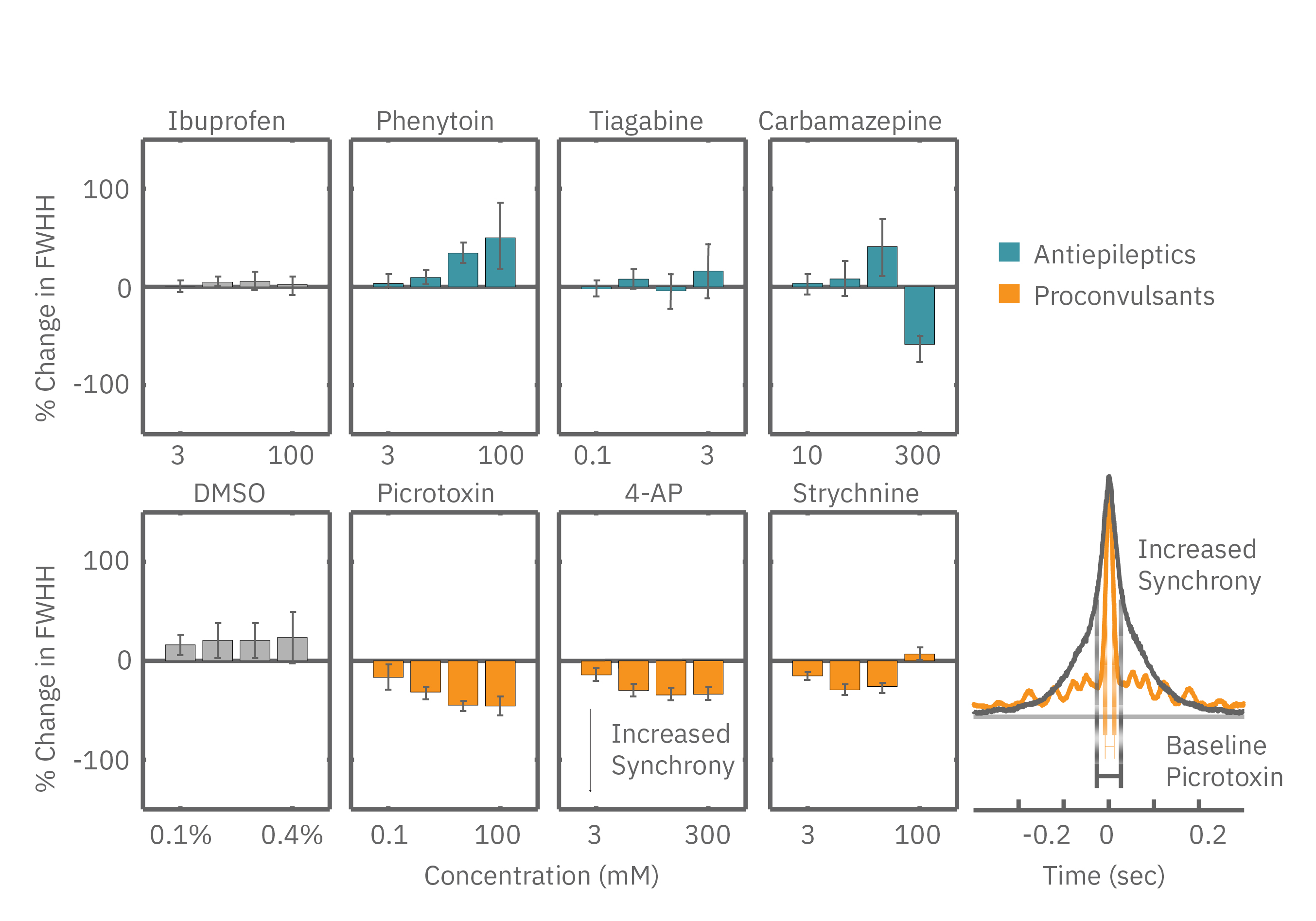
Maestro Pro、Edgeは、in vitro での神経活性化合物のハイスループット・スクリーニングに大変有用です (McConnel et al 2012, Valdivia et al 2014) 。複数電極での同時測定により、多くの解析エンドポイントが得られます。スパイク頻度などの基本的な解析項目は多くの神経活性化合物の評価に有用です。一方、ネットワークバースト(well 内の同期バースト) 、Synchrony (電極間に渡るスパイクの同期)などの解析指標は、痙攣などの誘発予測、或いは抑制の検証に有用です。本事例では、2枚の MEA プレートを用いて、16種類の化合物 (n=6)を評価しました。
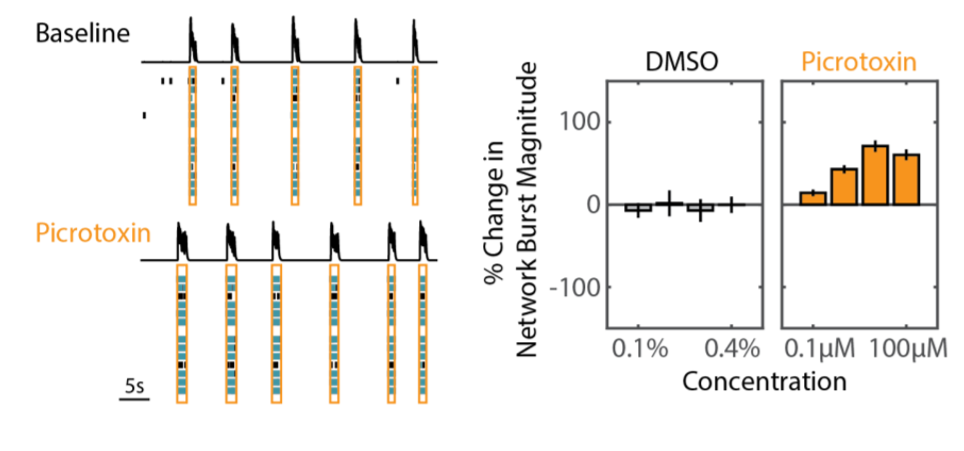
ネットワークバーストの大きさ(ネットワークバースト内のスパイク数)により、痙攣誘発化合物(例: Picrotoxin) とコントロール(DMSO) の差異が得られました (上図) 。
Synchrony 指標(例: full width at half height of the cross correlogram, FWHH) においても痙攣誘発化合物と抗てんかん/痙攣化合物が分離されました。痙攣誘発化合物の投与(下図、オレンジ色)では Synchrony の上昇が得られました。一方、抗てんかん/痙攣化合物の投与(下図 : 水色) により、Synchrony は減少しました。
神経活性化合物の影響は、神経機能、或いは細胞の健康状態、またはその両方に及ぶ可能性があります。細胞生存率を測定しなければ、神経毒性と細胞毒性を区別することは困難です。 Maestro では、同一電極を用いて、神経機能と細胞生存率の両方を評価することが可能です。
MEA Viabilityの詳細はこちらをご覧ください。
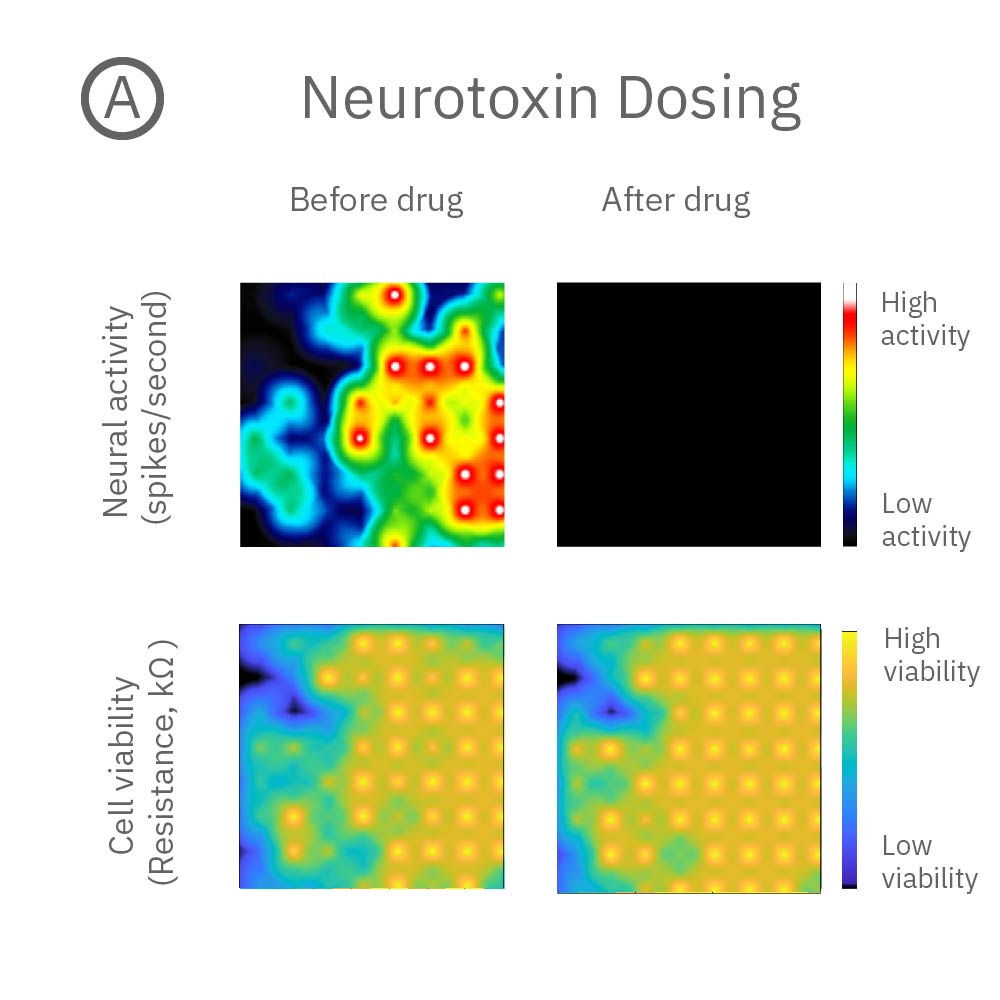
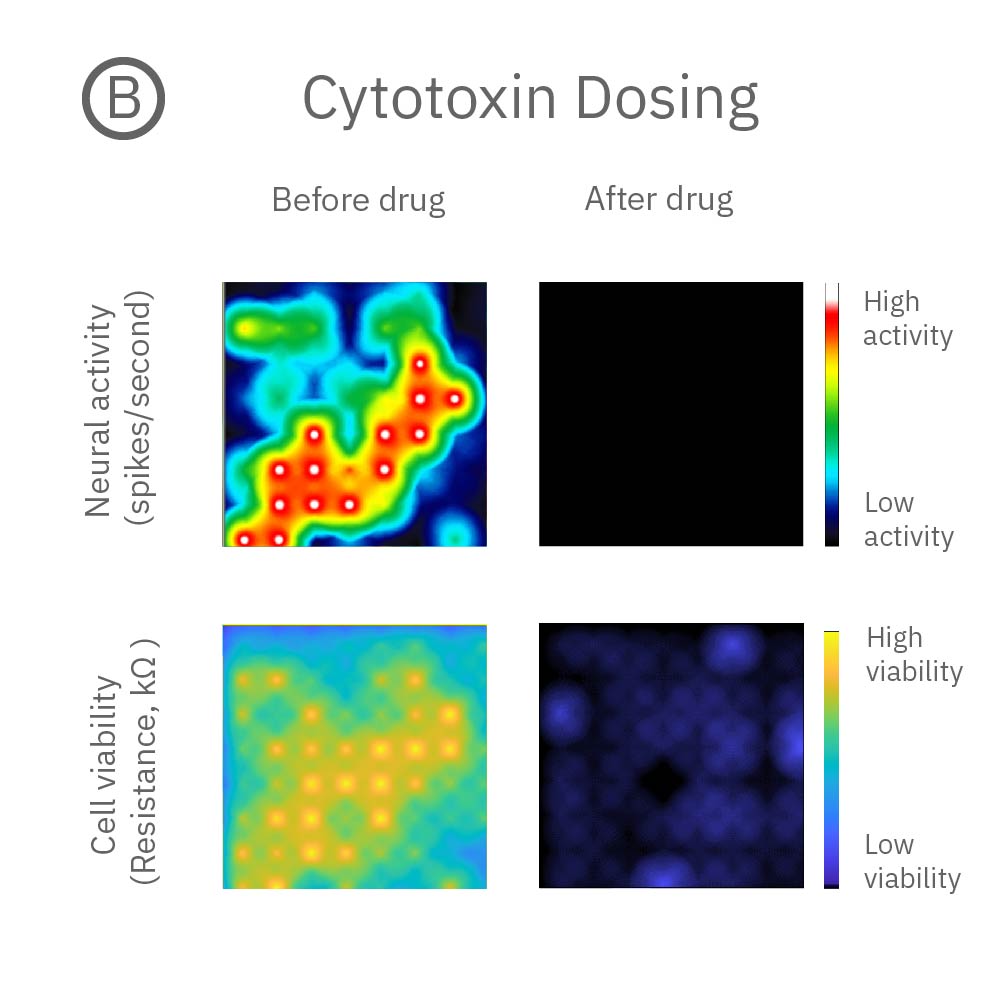
A: 神経毒性の例。投与後、神経活動は消失 (上段) したが、細胞生存率に影響は見られなかった(下段)。B: 細胞毒性の例: 投与後、神経活動(上段)、細胞生存率(下段)共に著しく減少した。
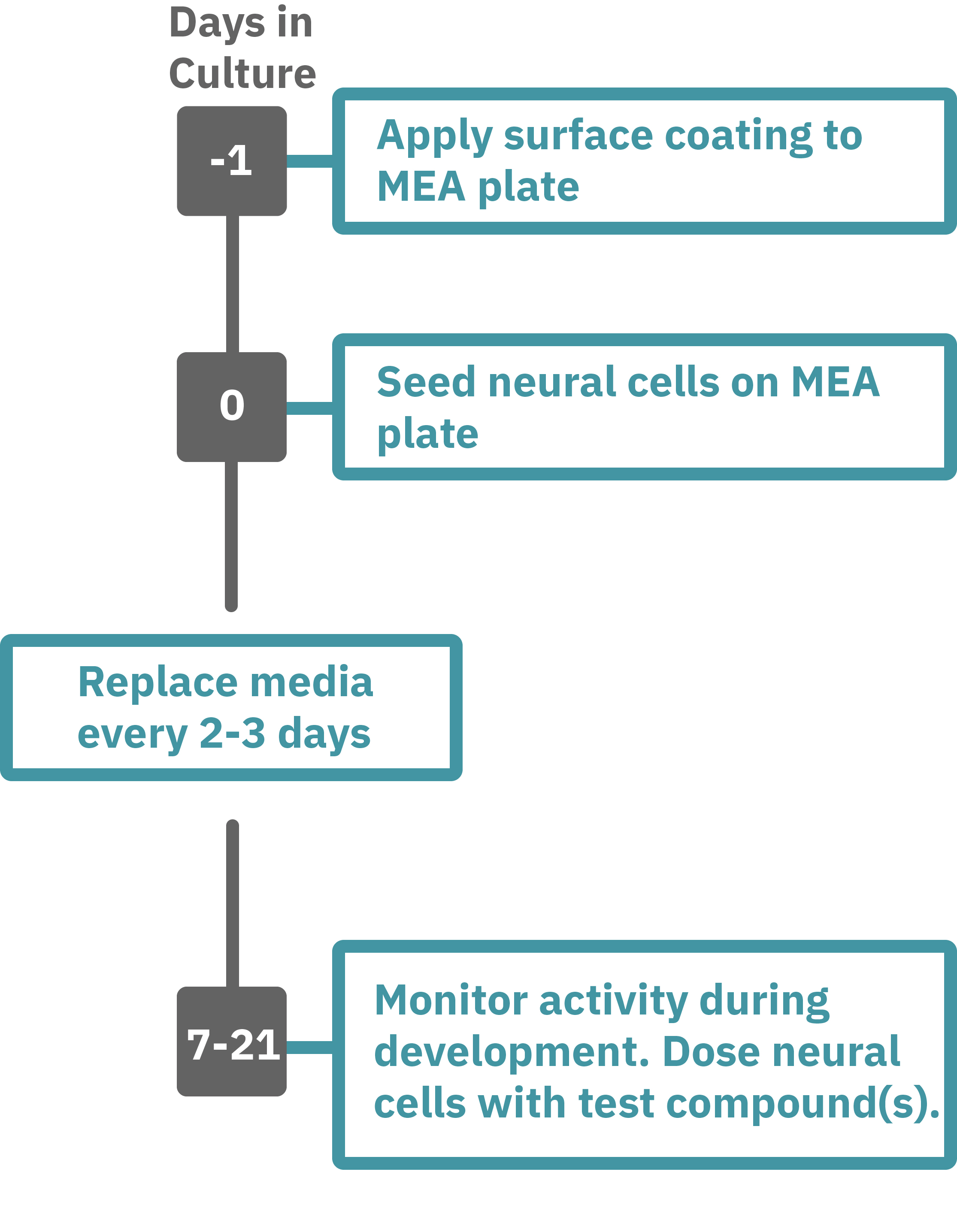
Getting started with Maestro Pro and Edge couldn't be easier. Culture your neurons in an Axion multiwell MEA plate (Day 0). Load the MEA plate into the Maestro MEA system at the desired recording times and begin recording. Analyze the neural activity in the MEA plate label-free and in real-time with AxIS Navigator Neural Module software. Add test compounds as required (e.g. Day 7).
Learn how to add MEA Viability to your protocol






